Orthopedic conditions
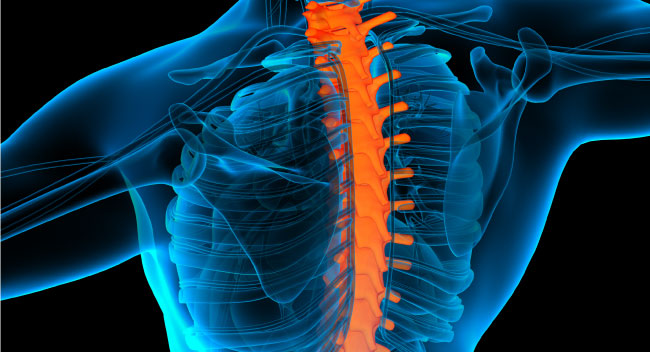
Spondylosis
Spondylosis is a medical term used to refer to the general degeneration of the spine and its shock-absorbing intervertebral discs. Degenerative changes may occur in the neck (known as the cervical region), middle back (thoracic region) or lower back (lumbar region) and tends to worsen with as an individual grows older. The United States currently sees more than 3 million cases of spondylosis per year, most of which usually appear in conjunction with other spinal issues. Spondylosis is a chronic condition that oftentimes lasts years or throughout a patient’s lifetime, but many people don’t have symptoms until the degeneration of the spinal column causes a secondary complication. While spondylosis can’t be cured, there are many advanced treatment options available to address the changes associated with this issue.
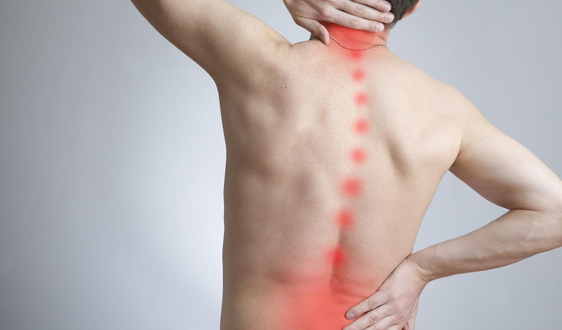
Back & neck pain
The most common cause of acute back or neck pain is a muscle injury, in which muscle fibers stretch too far and tear. Muscle injury may be caused by overuse, such as from heavy lifting, as well as by repetitive motions that put continual stress on the back or neck muscles.
While a muscle injury may not sound like a serious issue, the resulting pain can be severe. Most muscle injuries alleviate within 6 weeks using treatments such as over-the-counter pain medicines, heat or ice therapy, or stretching exercises.
Neck pain occurs in the area of the cervical vertebrae in your neck. Because of its location and range of motion, your neck is often left unprotected and subject to injury.
Back pain can range from a mild, dull, annoying ache, to persistent, severe, disabling pain. Pain in your back can restrict mobility and interfere with normal functioning and quality of life.
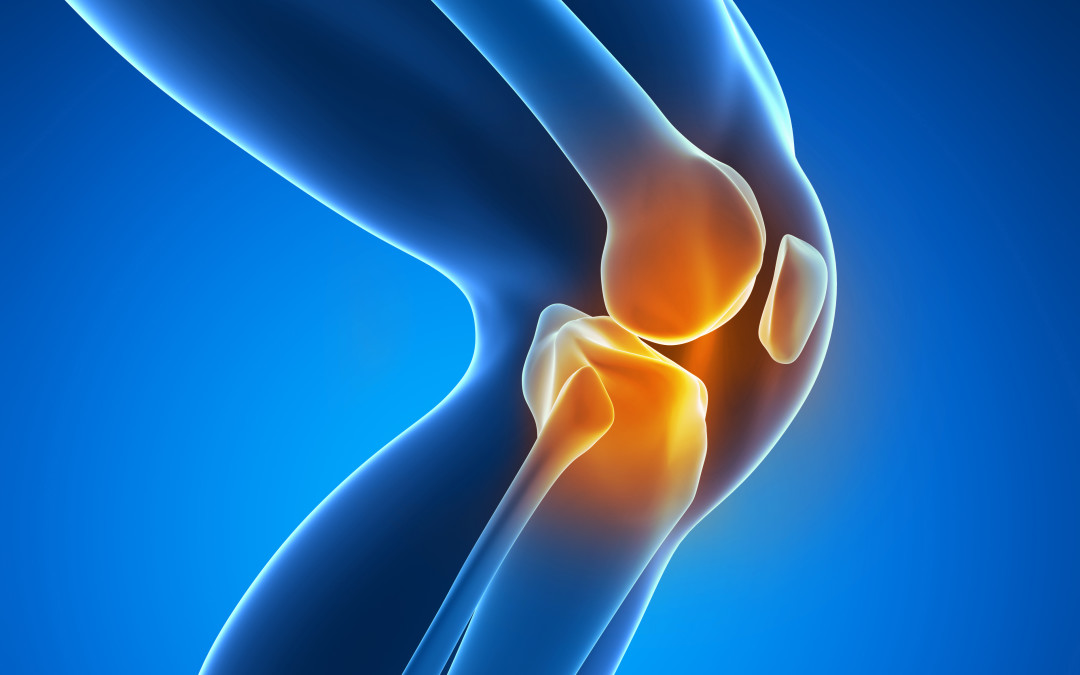
Arthritis knee pain
Arthritis is inflammation of one or more of your joints. Pain, swelling, and stiffness are the primary symptoms
of arthritis. Any joint in the body may be affected by the disease, but it is particularly common in the knee.
Knee arthritis can make it hard to do many everyday activities, such as walking or climbing stairs. It is a major cause of lost work time and a serious disability for many people.
The most common types of arthritis are osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, but there are more than 100 different forms. While arthritis is mainly an adult disease, some forms affect children.
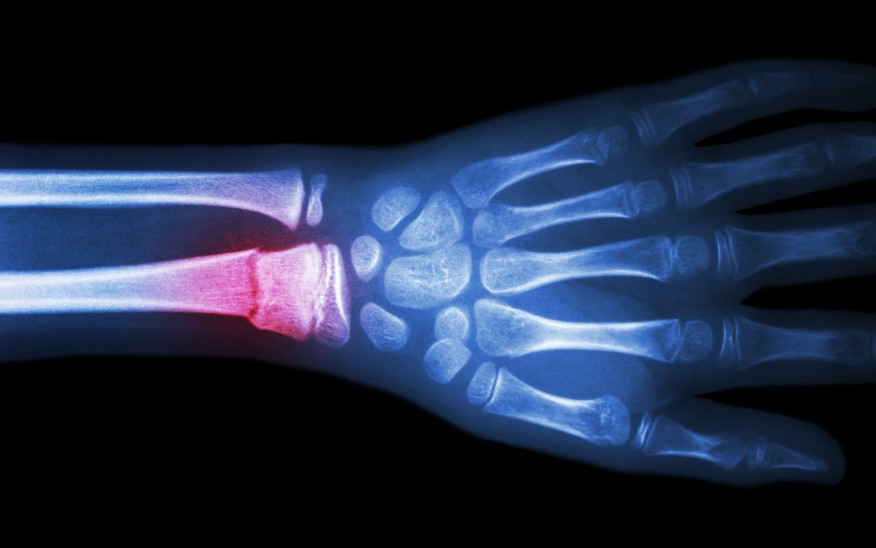
Fractures
A fracture is a break, usually in a bone. If the broken bone punctures the skin, it is called an open or compound
fracture. Fractures commonly happen because of car accidents, falls, or sports injuries. Other causes are low bone
density and osteoporosis,
which cause weakening of the bones. Overuse can cause stress fractures, which are very small cracks in the bone.
Your risk of fracture depends, in part, on your age. Broken bones are very common in childhood, although children's fractures are generally less complicated than fractures in adults. As you age, your bones become more brittle and you are more likely to suffer fractures from falls that would not occur when you were young.
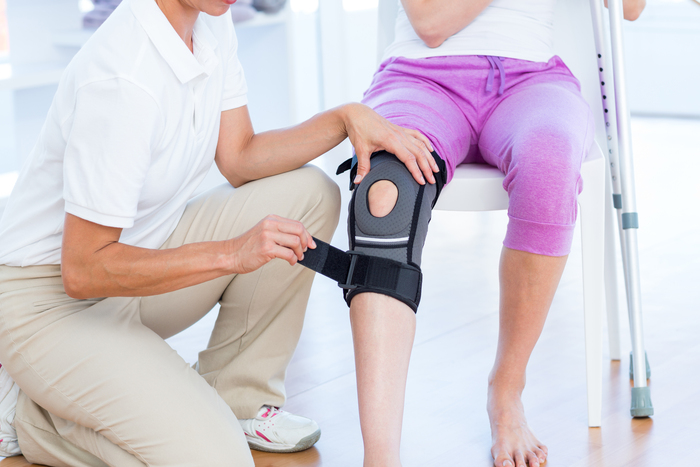

Post surgery physiotherapy
Post-orthopaedic surgery, you'll almost certainly require exercise progression to fully regain your strength,
flexibility and function. The quickest, safest and easiest
way to return to your day to day activities is by consulting a physiotherapist experienced
in post-operative rehabilitation.
At PhysioWorks, we'll happily assist you in your post-operative care. We are familiar with the treatment protocols prescribed by most Orthopapedic Surgeons in Brisbane. We'll happily liase with your surgeon to determine any specific requirements based on your individual surgery.
Frozen shoulder
Frozen shoulder, also known as adhesive capsulitis, is a condition characterized by stiffness and pain in your shoulder joint. Signs
and symptoms typically begin gradually, worsen over time and then resolve, usually within one to three years.
Your risk of developing frozen shoulder increases if you're recovering from a medical condition or procedure
that prevents you from moving your arm — such as a stroke or a mastectomy.
Treatment for frozen shoulder involves range-of-motion exercises and, sometimes, corticosteroids and numbing
medications injected into the joint capsule. In a small percentage of cases, arthroscopic surgery may be indicated
to loosen the joint capsule so that it can move more freely.
It's unusual for frozen shoulder to recur in the same shoulder, but some people can develop it in the opposite shoulder.